New Dazzling And Mystifying Images Of Pluto in Technicolor!
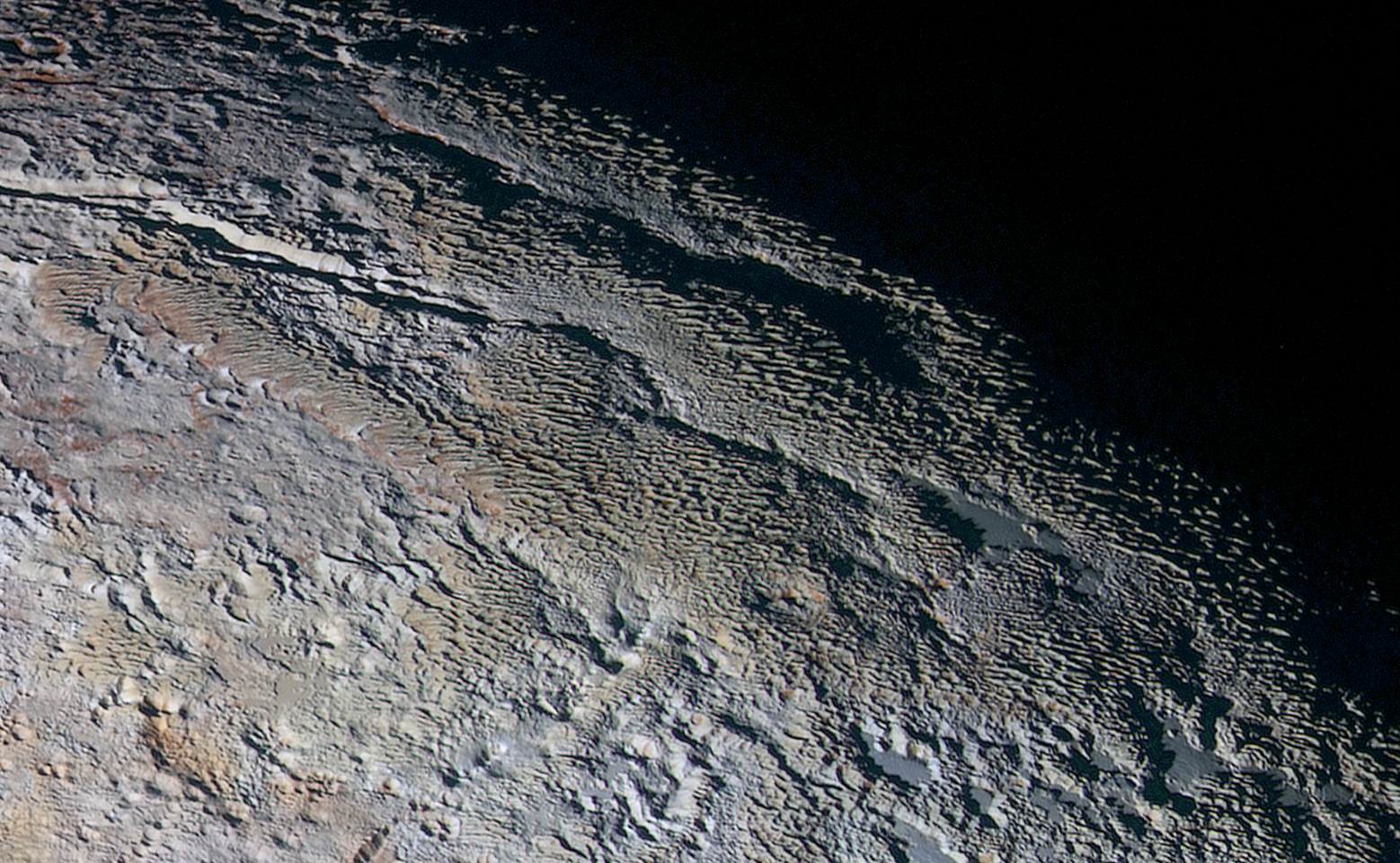
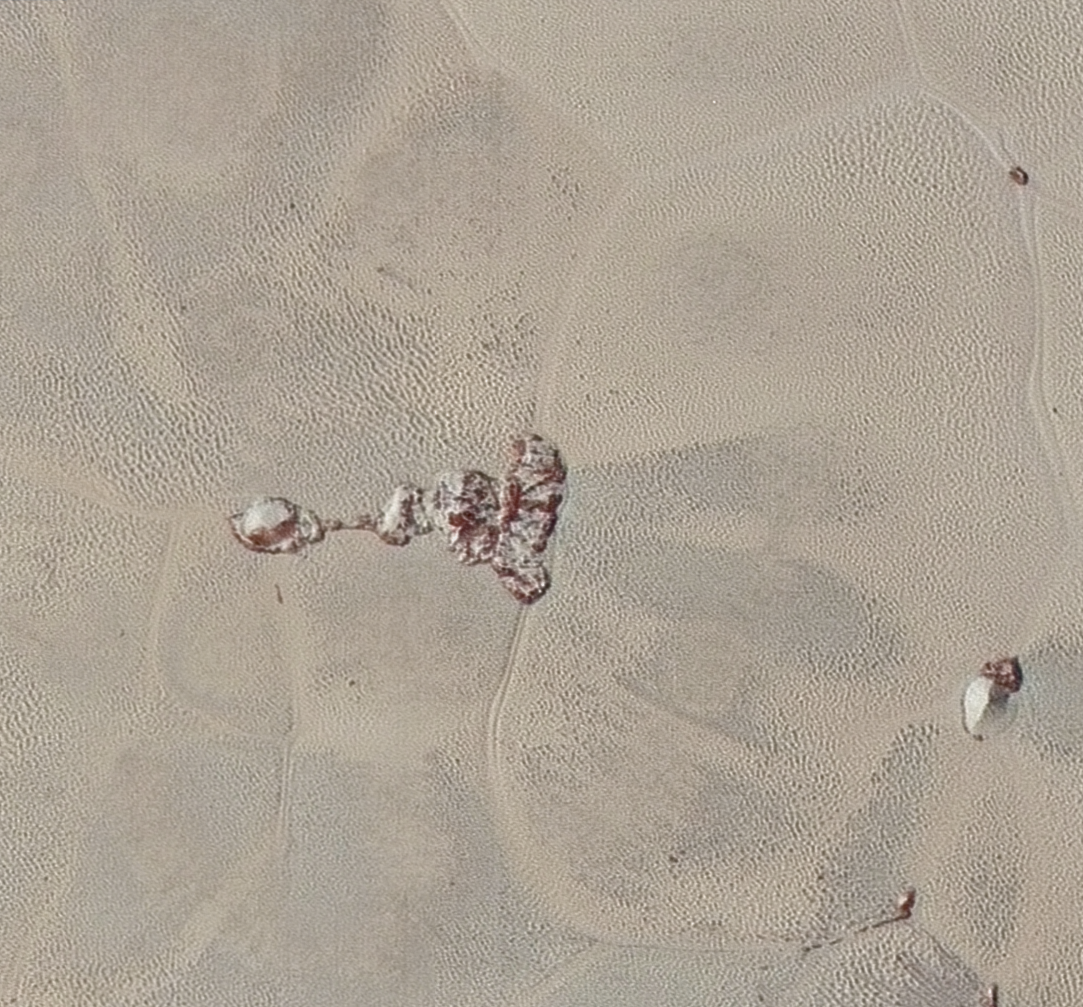

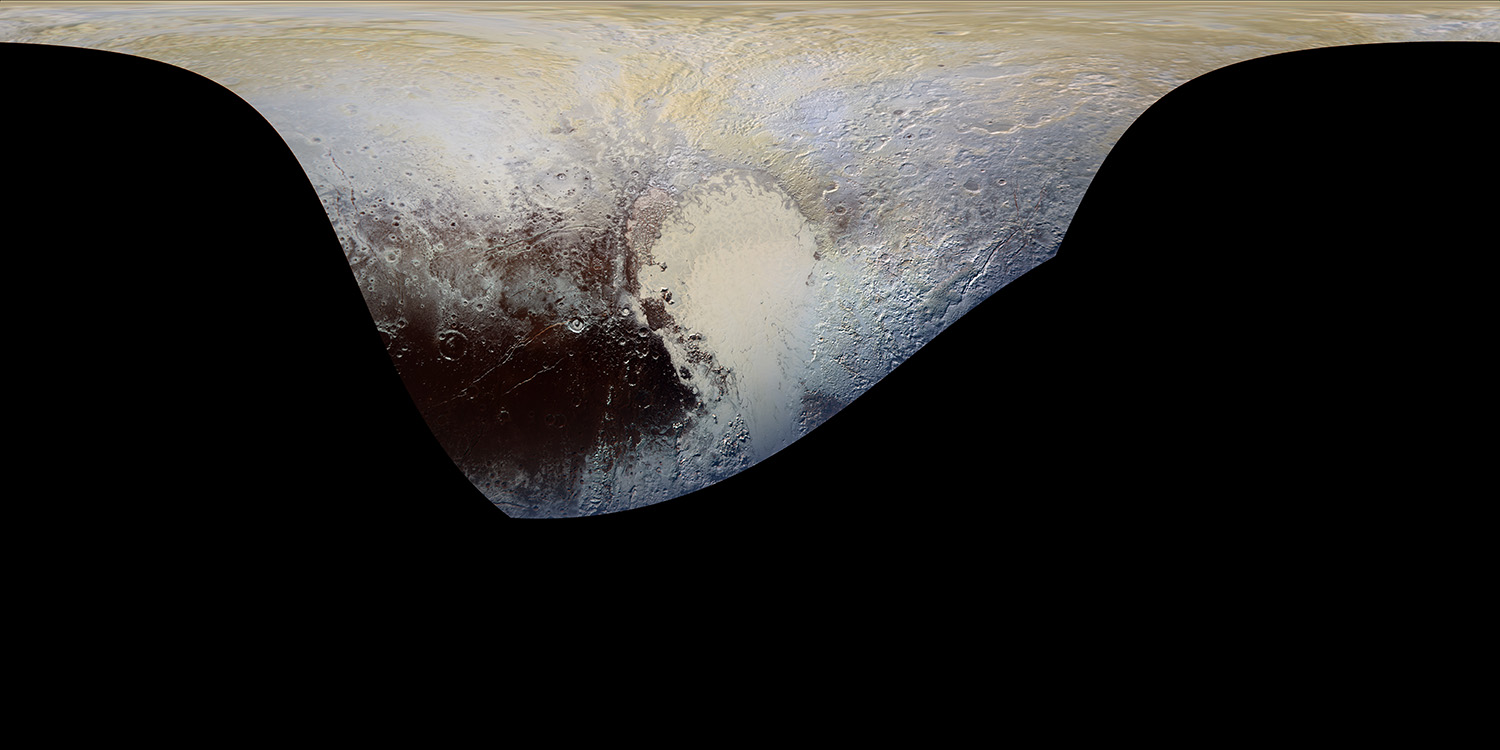


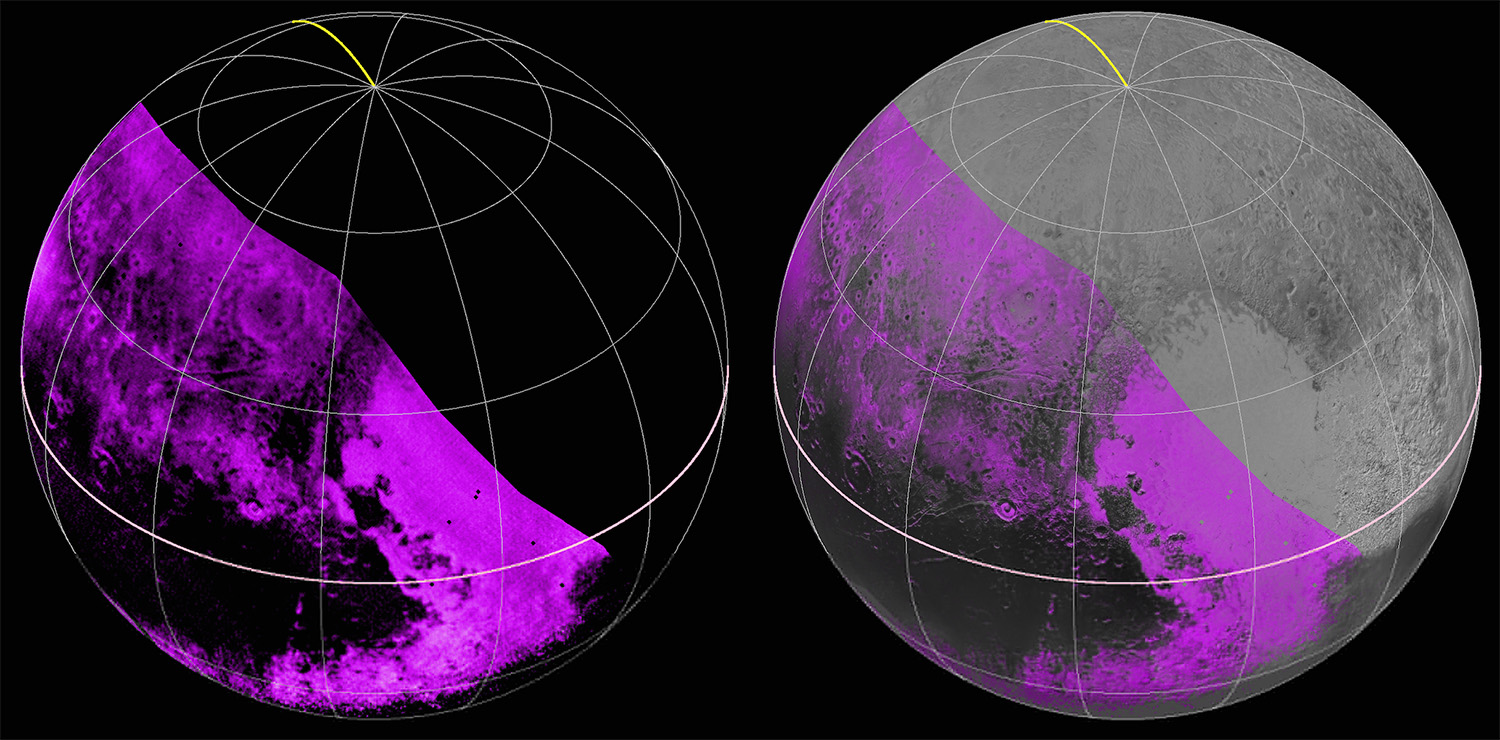
For the original Pluto press release, click here.





For the original Pluto press release, click here.

To access the full features of Pluto Safari please download the FREE app for iOS from the Apple App Store or Pluto Safari: New Horizons for Android from Google Play.
Alternatively, if you have SkySafari or Pluto Safari installed you could download the simulation settings file here.